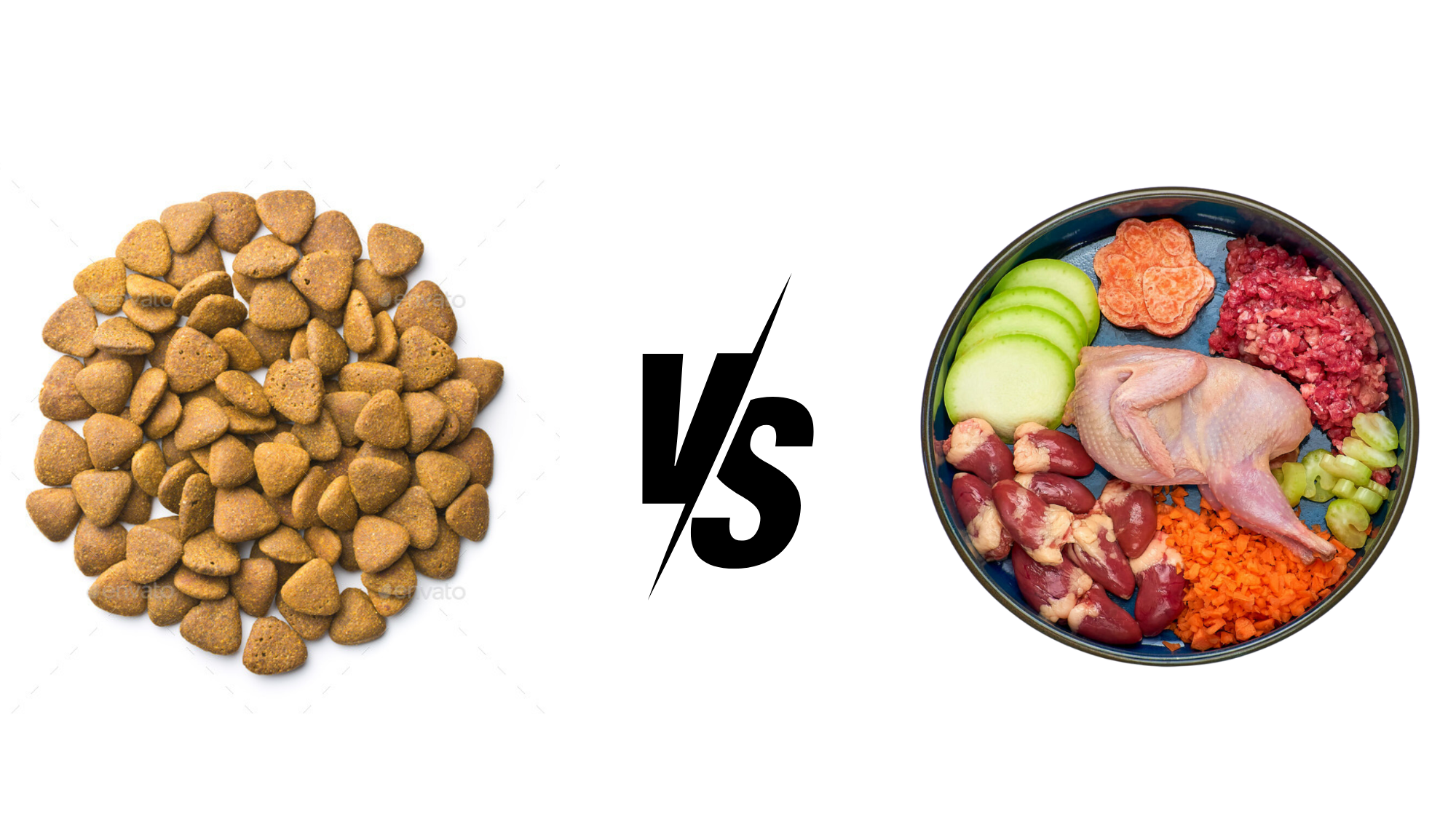
| Summary: Kibble offers convenience, affordability, and balanced nutrition, while a raw diet provides natural, high-quality nutrients and better digestion. Raw feeding supports dental health but requires careful planning. Kibble suits busy owners, whereas raw is ideal for optimal health. Choose based on your dog’s needs, lifestyle, and budget. |
Choosing the right diet for your dog is one of the most important decisions you’ll make as a pet owner. With so many options available, two of the most debated choices are kibble (commercial dry dog food) and the raw diet (also known as the BARF—Biologically Appropriate Raw Food—diet). Both kibble vs raw diet for dogs have loyal advocates who argue their benefits, but which one truly supports your dog’s health, longevity, and well-being?
Explore the best dog collars for French Bulldogs to keep them comfortable while ensuring durability and style.
Some dog owners swear by kibble for its convenience, affordability, and nutritional completeness, while others claim that a raw diet is more natural, species-appropriate, and beneficial for a dog’s digestion and energy levels. However, each option has pros and cons, and the best choice depends on your dog’s breed, lifestyle, and health needs.
In this guide, we’ll compare kibble vs raw diet for dogs in terms of nutrition, digestion, dental health, cost, convenience, and overall impact on well-being to help you make an informed decision.
| Factor | Kibble | Raw Diet |
| Nutritional Value | Balanced but processed, may contain fillers and additives. | High-quality, natural nutrients but requires careful planning. |
| Digestibility | Can be harder to digest, may contain grains and synthetic ingredients. | Easier to digest, promotes better gut health. |
| Dental Health | May leave residue, leading to plaque buildup. | Naturally cleans teeth, reduces tartar and plaque. |
| Food Safety | Processed at high temperatures, lower bacterial risks. | Risk of bacteria like Salmonella; requires proper handling. |
| Cost | More affordable and widely available. | More expensive, especially high-quality raw food. |
| Convenience | Easy to store, feed, and travel with. | Requires meal prep, proper storage, and refrigeration. |
| Allergy Potential | Some dogs react to grains, fillers, or artificial additives. | Fewer allergens due to the absence of artificial ingredients. |
| Stool & Gut Health | Larger, smellier stools due to fillers and less absorption. | Smaller, firmer stools due to better nutrient absorption. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint due to processing and packaging. | More sustainable if using ethically sourced meats. |
| Best For | Busy owners, budget-conscious pet parents. | Owners prioritizing optimal nutrition and natural diets. |
| Final Verdict | ✅ Best for convenience and affordability. | ✅ Best for overall health and digestion (if properly balanced). |
Blog Highlights
Toggle1. Nutritional Differences: Kibble vs Raw Diet For Dogs
Kibble Nutrition
Kibble is a processed dry food designed to provide balanced nutrition for dogs. High-quality kibble includes a mix of protein, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, formulated to meet AAFCO (Association of American Feed Control Officials) guidelines.

✔ Balanced nutrients: Most kibble brands are fortified with essential vitamins and minerals to meet a dog’s dietary requirements.
✔ Protein sources vary: Some brands use high-quality animal proteins, while others rely on meat by-products or plant-based proteins.
✔ Carbohydrates are prominent: Many kibble formulas contain grains, potatoes, or legumes as their primary energy source.
✔ Preservatives and additives: To extend shelf life, kibble often contains synthetic preservatives, artificial colors, and fillers.
Concerns with Kibble Nutrition
While kibble is designed to be nutritionally complete, some pet owners worry about low-quality ingredients and high carbohydrate content in cheaper brands. Many mass-market kibbles contain:
❌ Fillers and by-products with minimal nutritional value.
❌ Artificial additives that may cause allergies or sensitivities.
❌ Lower moisture content, leading to dehydration risks.
Raw Diet Nutrition
A raw diet typically consists of raw meat, bones, organs, and sometimes fruits and vegetables. Advocates claim this mimics what dogs ate in the wild, providing superior nutrition compared to processed kibble.
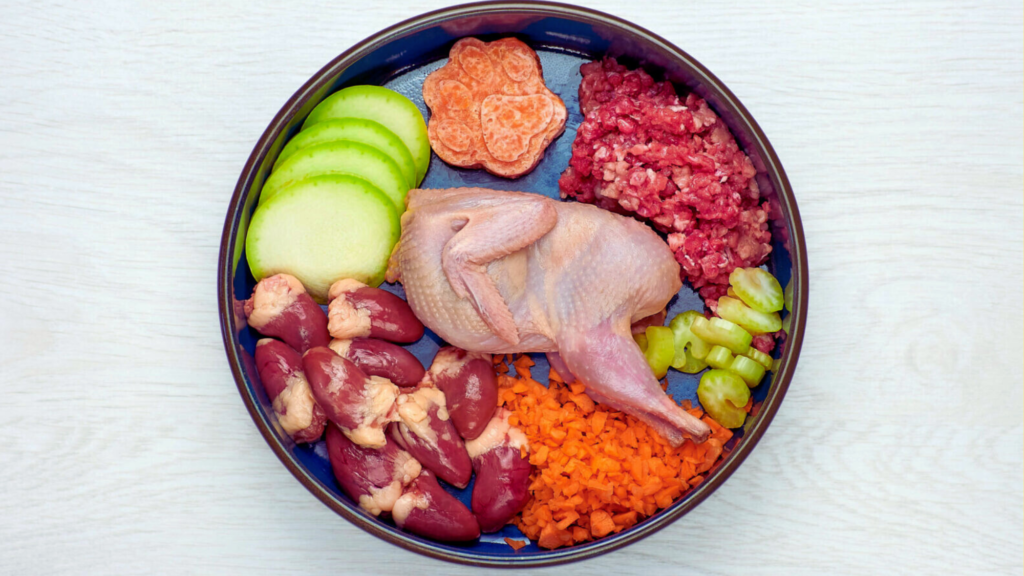

✔ High in protein: Raw food is rich in real animal protein, essential for muscle development.
✔ Minimal carbohydrates: Unlike kibble, raw diets avoid grains and fillers, making them a low-carb alternative.
✔ Natural vitamins and minerals: Whole foods provide bioavailable nutrients without synthetic additives.
✔ Healthy fats: Raw diets often include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which support skin, coat, and brain health.
Concerns with Raw Diet Nutrition
Despite its benefits, a raw diet can be nutritionally unbalanced if not carefully planned. Some risks include:
❌ Deficiencies in calcium, phosphorus, or essential vitamins if meals aren’t properly formulated.
❌ Excessive fat intake from fatty meats, leading to pancreatitis.
❌ Potential over-reliance on muscle meat without including organs and bones for balance.
✅ Winner: Raw Diet for natural, high-quality nutrients, but requires careful meal planning to avoid deficiencies.
Find the best dog collars for Dachshunds that accommodate their long bodies and prevent strain on their necks.
2. Digestibility & Gut Health
Kibble Digestibility
Kibble takes longer to digest due to processed carbohydrates and synthetic ingredients. While some high-quality kibble brands use digestible proteins, many contain corn, wheat, and soy, which can be difficult for some dogs to break down.
✔ Easy to store and feed, but some ingredients may be harder to digest.
✔ Often linked to food allergies in sensitive dogs.
✔ May cause bloating or gas, especially if dogs eat too quickly.
Raw Diet Digestibility
Raw food is easier for dogs to digest because it is less processed and closely resembles their ancestral diet. Dogs on a raw diet typically have:
✔ Smaller, firmer stools due to better nutrient absorption.
✔ Less bloating and gas, as raw food lacks fermentable fillers.
✔ Improved gut microbiome, promoting healthier digestion.
✅ Winner: Raw Diet for easier digestion and better gut health.
3. Dental Health: Kibble vs. Raw
Kibble & Dental Health
Many pet food companies claim that kibble helps clean a dog’s teeth, but in reality, most kibble is too soft to remove tartar effectively. Some dental kibbles are formulated for better oral health, but standard kibble often:
❌ Leaves residue on teeth, leading to plaque buildup.
❌ Contains starchy ingredients, which feed oral bacteria.
Raw Diet & Dental Health
Raw diets naturally clean teeth, especially when dogs chew on raw meaty bones. Benefits include:
✔ Prevention of plaque and tartar buildup.
✔ Stronger jaw muscles from chewing raw bones.
✔ Healthier gums and fresher breath.
✅ Winner: Raw Diet, as chewing raw bones naturally improves oral hygiene.
4. Safety Concerns & Risks
Kibble Safety Risks
While kibble is cooked at high temperatures, reducing bacterial risks, it can still pose dangers:

❌ Risk of mold or contamination, leading to recalls.
❌ Preservatives and artificial additives may cause long-term health issues.
Raw Diet Safety Risks
The biggest concern with raw feeding is the risk of bacteria (like Salmonella or E. coli). However, handling raw food properly minimizes risks.
❌ Improper storage may lead to contamination.
❌ Unbalanced meals can cause nutritional deficiencies.
✅ Winner: Kibble for food safety, but proper handling of raw food can make it equally safe.
Get insights into what is best for Dachshunds: a collar or harness for their safety, comfort, and health during walks.
5. Cost & Convenience
Kibble Cost & Convenience
✔ More affordable, especially budget brands.
✔ Easy to store and travel with.
✔ Requires no preparation.
Raw Diet Cost & Convenience
❌ More expensive, especially for high-quality meats.
❌ Requires meal prep and storage space.
✔ More natural and beneficial long-term.
✅ Winner: Kibble for cost-effectiveness and convenience.
6. Digestibility and Nutrient Absorption
How Kibble Affects Digestion
Kibble is designed to have a long shelf life, which means it undergoes high-temperature processing that can alter the natural structure of proteins and nutrients. This can make it harder for dogs to digest and absorb essential nutrients. Many kibble formulas include synthetic vitamins and minerals to compensate for what is lost during processing, but these may not be as bioavailable as natural sources found in fresh food.
Additionally, kibble often contains fillers such as corn, wheat, and soy, which some dogs struggle to digest. These ingredients can contribute to bloating, gas, and loose stools, particularly in dogs with sensitive stomachs. Since kibble is dry, dogs must drink more water to aid digestion, but some dogs may not consume enough, leading to mild dehydration over time. This can also increase the risk of kidney and urinary tract issues.
Raw Food and Digestibility
Raw diets are highly digestible because they contain fresh, unprocessed ingredients that dogs are naturally adapted to eat. Since raw food is rich in moisture and natural enzymes, it supports easier digestion and better nutrient absorption. Dogs on a raw diet typically produce smaller, firmer stools because their bodies utilize more of the nutrients, leaving behind less waste.
Another benefit of raw feeding is the reduced likelihood of food allergies and intolerances. Since raw diets avoid artificial preservatives, additives, and excessive carbohydrates, they are less likely to cause digestive upset.
Many dog owners report improved gut health, fewer instances of diarrhea, and better overall digestion after switching to a raw diet. However, it is important to ensure the diet is balanced to prevent nutritional deficiencies.
To discover what activities bring joy to Australian Cattle Dogs, check out this detailed guide on What Do Australian Cattle Dogs Love.
7. Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The Environmental Footprint of Kibble
The commercial pet food industry has a significant environmental impact due to mass production, packaging waste, and the resources required to manufacture kibble. Many kibble brands use low-quality meat by-products and grains that come from large-scale industrial farming, which contributes to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and excessive water usage. The production and transportation of kibble also increase carbon footprints, making it less environmentally friendly.
Additionally, the packaging of kibble is often made from plastic or non-recyclable materials, which adds to environmental pollution. Since kibble requires preservatives to maintain its shelf life, the processing methods also contribute to energy consumption and waste production. Choosing sustainably sourced kibble brands or those that use eco-friendly packaging can help reduce the environmental impact, but it remains a challenge compared to fresh food options.
Raw Feeding and Sustainability
Raw feeding, when done responsibly, can be a more sustainable option, especially when using ethically sourced meat or locally available ingredients. Many raw feeders opt for grass-fed, free-range, or humanely raised meats, which have a lower environmental impact compared to factory-farmed products. Some dog owners also reduce waste by feeding organ meats and bones that would otherwise be discarded by the meat industry.
However, raw feeding can also be resource-intensive if not approached sustainably. Buying individually packaged raw meals or exotic meats increases the environmental footprint. To minimize impact, some raw feeders choose to source meat from local farms, butcher shops, or even use food scraps from human-grade cuts to reduce waste. Home-prepared raw diets also eliminate plastic packaging, making them a more eco-friendly alternative.
Which Diet Is Right for Your Dog: Kibble vs Raw Diet For Dogs

- For busy owners who need convenience: Kibble is the better choice.
- For dogs with allergies or sensitivities: Raw diet is often better.
- For dental health benefits: Raw diet wins.
- For cost-conscious pet owners: Kibble is cheaper.
- For superior nutrition: Raw food, if properly balanced, is best.
✅ Final Verdict: Raw Diet is ideal for optimal health, but Kibble is easier for most owners.
To find the ideal collar size for your Australian Cattle Dog, check out this guide on What Size Collar for Australian Cattle Dog for helpful tips on measurement and fit recommendations.
FAQs
1. Is raw feeding safe for all dogs?
Raw feeding can be safe if properly balanced, but puppies, senior dogs, and immunocompromised dogs may need extra precautions.
2. Can I mix kibble and raw food?
Yes, but digestive enzymes differ. It’s best to feed them separately to avoid stomach upset.
3. Does kibble cause allergies?
Some dogs develop allergies to grains, fillers, or artificial additives in kibble.
4. Will a raw diet make my dog aggressive?
No, raw feeding does not increase aggression. That’s a myth.
5. Do vets recommend raw feeding?
Opinions vary. Some support raw diets, while others worry about nutritional imbalances and bacteria risks.
6. Which diet is best for dogs with sensitive stomachs?
A well-balanced raw diet is often easier to digest than kibble.
7. How can I transition my dog from kibble to raw food?
Transition gradually over 7-10 days, mixing increasing amounts of raw food with kibble.





